Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-032, 159 Pages, 2024/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2022, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near- field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 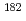 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/07
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the medium- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2022 (April 1st, 2022 - March 31st, 2023) and their evaluation by the committee.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Sakai, Akihiro
Dai-33-Kai Genshiryoku Shisetsu Dekomisshoningu Gijutsu Koza Tekisuto, p.31 - 63, 2023/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is promoting the project for concrete-vault disposal and landfill-type disposal of radioactive waste generated from research facilities, etc. This report introduces current status of technical development for JAEA's disposal project as following items; (1) kinds of research facilities and characteristics of radioactivity inventory of the waste, (2) the structures of the disposal facilities which JAEA conceptually designed, (3) development of waste acceptance criteria for major radioactive waste for the JAEA disposal facilities, (4) the concept of the criteria for disposal of uranium bearing waste, that has been established in 2021.
Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-025, 164 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2021, we continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Planning and Co-ordination Office, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-008, 68 Pages, 2022/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) consulted an assessment committee, "Evaluation Committee of Research and Development (R&D) Activities for Nuclear Safety Research", for post-review and pre-review assessments of Nuclear Safety Research, in accordance with "General Guideline for Evaluation of Government R&D Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, "Guideline for Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by JAEA. In response to the JAEA's consult, the Committee assessed the results and outcomes of the R&D programs during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan (from April 2015 to March 2022, including the expected results and outcomes) and the validity of the 4th mid-/long-term plan (7 years from FY2022), according to the above-mentioned guidelines. The Committee concluded that the rationale behind the R&D programs, the relevance of the program outcome and the efficiency of the program implementation during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan are comprehensively evaluated as "A", and the R&D programs for the 4th mid-/long-term plan is generally appropriate. This report summarizes the results of the assessment by the Committee. In addition, the appendices of the report contain the responses from JAEA on the comments and suggestions by the Committee and the presentation materials submitted to the Committee.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-004, 38 Pages, 2022/11
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the mid- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2021 (April 1st, 2021 - March 31st, 2022) and their evaluation by the committee.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-003, 61 Pages, 2022/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (hereinafter referred to as "JAEA") consults an assessment committee, "Evaluation Committee of Research Activities for Computational Science and Technology Research" (hereinafter referred to as "Committee") for result and in-advance evaluation of "Computational Science and Technology Research", in accordance with "General Guideline for the Evaluation of Government Research and Development (R&D) Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, "Guideline for Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by the JAEA. In response to the JAEA's request, the Committee assessed the research program of the Center for Computational Science and e-Systems (hereinafter referred to as "CCSE"). The Committee evaluated the management and research activities of the CCSE based on explanatory documents prepared by the CCSE, and oral presentations with questions-and answers.
Mineo, Hideaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(11), p.617 - 621, 2022/11
, 64(11), p.617 - 621, 2022/11
In December 2016 Decisions were made by the Government on the Fast Breeder Prototype Reactor "Monju", which were decommissioning of the reactor and installation of a new research reactor at the Monju site. After the decisions, MEXT started research to list reactor candidates suitable for the site. Among the candidates, medium power reactor type of which thermal output less than 10,000 kW was chosen to utilize neutron beams. Then, from 2020, MEXT launched an entrusted business and adopted JAEA, Kyoto University and University of Fukui as the core institutions of the business to carry out the conceptual design. This paper describes the system to proceed the conceptual design and to examine the utilization management of the new research reactor and also shows their status.
Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2022-017, 113 Pages, 2022/08
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017. The activation activity of radioactive materials remaining in the reactor facility was evaluated in order to submit the decommissioning plan to the Nuclear Regulation Authority. Total activation activity was 9.3 10
10 Bq after the permanent shutdown of reactor, 2.7
Bq after the permanent shutdown of reactor, 2.7 10
10 Bq after 21 years, 1.0
Bq after 21 years, 1.0 10
10 Bq after 40 years and 2.4
Bq after 40 years and 2.4 10
10 Bq after 100 years. The structure with high activation activity was the core structural materials in JMTR such as beryllium frame, aluminum reflector, etc., and the material was stainless steel, beryllium, etc. The ratio of nuclides to the total amount of activated radioactivity was highest in H-3 until about 40 years after the reactor shutdown, and then in Ni-63. For reference, the radioactivity level was classified based on the results of the obtained radioactivity concentration. The ratio of the weight of each radioactivity level to the total weight was 0.3-0.4% (10-13t) for L1, 0.0-0.4% (0-14t) for L2, 1.0-1.2% (32-39t) for L3 and 98.0-98.7% (about 3200t) for CL until 100 years after the reactor shutdown. It was found that those classified as CL account for more than 90% of the total. When treating and disposing of radioactive waste, evaluation will be carried out based on appropriate methods, including evaluation results of secondary pollutants.
Bq after 100 years. The structure with high activation activity was the core structural materials in JMTR such as beryllium frame, aluminum reflector, etc., and the material was stainless steel, beryllium, etc. The ratio of nuclides to the total amount of activated radioactivity was highest in H-3 until about 40 years after the reactor shutdown, and then in Ni-63. For reference, the radioactivity level was classified based on the results of the obtained radioactivity concentration. The ratio of the weight of each radioactivity level to the total weight was 0.3-0.4% (10-13t) for L1, 0.0-0.4% (0-14t) for L2, 1.0-1.2% (32-39t) for L3 and 98.0-98.7% (about 3200t) for CL until 100 years after the reactor shutdown. It was found that those classified as CL account for more than 90% of the total. When treating and disposing of radioactive waste, evaluation will be carried out based on appropriate methods, including evaluation results of secondary pollutants.
Kochiyama, Mami; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-009, 56 Pages, 2022/06
It is necessary to evaluate radioactivity inventory in wastes before disposal of low-level radioactive wastes generated from dismantling research reactors. It is efficient for owners of each research reactor to use a common radioactive evaluation method in order to comply with the license application for disposal facility. In this report, neutron transport and activation calculations were carried out for the Rikkyo University research reactor in order to examine a common radioactivity evaluation method for burial disposal of radioactive wastes generated by dismantling. We adopted the neutron transport codes DORT and MCNP and the activation code ORIGEN-S with cross-section libraries based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017. The radioactivity concentrations obtained by the radiochemical analysis and both calculation codes were in agreement by 0.4 to 3 times. Therefore, by appropriately considering this difference, the radioactivity evaluation method by DORT, MCNP and ORIGEN-S can be applied to the radioactivity evaluation for buried disposal. In order to classify wastes from dismantling by clearance or buried disposal method according to their radioactivity levels, we also created radioactivity concentration distributions in the concrete area and graphite thermal column area.
Task Force on Maintenance Optimization of Nuclear Facilities
JAEA-Technology 2022-006, 80 Pages, 2022/06
The Task force on maintenance optimization of nuclear facilities was organized in the Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) since November 2020, in order to adequately respond to "the New nuclear regulatory inspection system since FY 2020" and to continuously improve the facility maintenance activities. In 2021, the task force has studied (1) optimization of the importance classification on maintenance and inspection of nuclear facilities, and (2) improvement in setting and evaluation of the performance indicators on safety, maintenance and quality management activities, considering "the Graded approach" that is one of the basic methodologies in the new nuclear regulatory inspection system. Each nuclear facility (research reactors, nuclear fuel material usage facilities, others) in the NSRI will steadily improve their respective safety, maintenance and quality management activities, referring the review results suggested by the task force.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2021-067, 135 Pages, 2022/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each departments manage facilities and develop related technologies to achieve the "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2017 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by the Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Materials Sciences Research Center, and development activities of Nuclear Human Resources Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2021-053, 133 Pages, 2022/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2020, JAEA continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on nearfield system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, 'full scale engineered barrier system (EBS) experiment' and 'solute transport experiment' were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". 'Development and testing of EBS emplacement / retrieval and tunnel closure technologies' and 'evaluation of EBS behavior over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Keio University*
JAEA-Review 2021-048, 181 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study of corrosion and degradation of the objects in the nuclear reactor by microorganisms" conducted in FY2019 and FY2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for two fiscal years were summarized. The purpose of the study is to obtain knowledge related to microorganisms that will be useful in the decommissioning process of 1F. Therefore, we clarified the current conditions of the microbial community inhabiting the power plant and its premises. Environmental samples were taken from several sites such as, topsoil from the south of the plant site boundary (south of the treated water tanks), seabed soil and its above water near the plant, surface water 3km offshore …
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2021-006, 248 Pages, 2021/12
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Fukushima Technology Development and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Middle and long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2015 and 2016 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Nuclear Safety Research Center, Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Material Science Research Center, and development activities of Nuclear Human Resources Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Planning and Co-ordination Office, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Review 2021-019, 58 Pages, 2021/11
In response to the directives of the 4th medium-to-long-term objectives, Japan Atomic Energy Agency will formulate the 4th medium-to-long-term plan and run its operation according to the plan from the fiscal year 2022. Consequently, the Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness has reviewed the strategies of the safety research for contributing to the demand, "the continuous improvement of nuclear safety and the effectiveness of nuclear disaster prevention". It was also discussed how to proceed the safety research over the medium-to-long-term plan period based on the proposed new strategies. From the viewpoint of developing human resources and maintaining research capabilities in the sector, discussion was made on measures to pass on the knowledge and skills of senior and mid-career researchers to young researchers. The main elements of the proposed strategies are: (1) to efficiently and effectively develop both problem-solving research and advanced or leading research, considering the importance and needs on the nuclear safety and corresponding to regulatory trends and introduction of new technologies, (2) to produce research results of high quality for social implementation, including proactive proposal of measures for enhancing rationality of nuclear safety and regulation by utilizing risk information, and (3) to promote development of human resources and maintenance of technological base through challenging new research subjects. This report summarizes results of the discussion on the medium-to-long-term safety research strategies and the research plans based on the proposed strategies.
Department of HTTR
JAEA-Review 2021-017, 81 Pages, 2021/11
The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is the first High-Temperature Gas cooled Reactor (HTGR) constructed in Japan at the Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency with 30MW in thermal power and 950 C of outlet coolant temperature. The purpose of the HTTR is to establish and upgrade basic technologies for HTGRs. The HTTR has accumulated a lot of experience of HTGRs' operation and maintenance up to the present time throughout rated power operations, safety demonstration tests, long-term high temperature operations and demonstration tests relevant to HTGRs' R&Ds. In the fiscal year 2019, we continued to make effort to restart operations of the HTTR that stopped since the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. It is necessary for the HTTR reoperation to prove conformity with the new regulatory requirements for research reactors enacted in December 2013. So we might cope with government agency to pass the inspection of application document for the HTTR licensing. This report summarizes the activities carried out in the fiscal year 2019, which were the situation of the new regulatory requirements screening of the HTTR, the operation and maintenance of the HTTR, R&Ds relevant to commercial-scale HTGRs, the international cooperation on HTGRs and so on.
C of outlet coolant temperature. The purpose of the HTTR is to establish and upgrade basic technologies for HTGRs. The HTTR has accumulated a lot of experience of HTGRs' operation and maintenance up to the present time throughout rated power operations, safety demonstration tests, long-term high temperature operations and demonstration tests relevant to HTGRs' R&Ds. In the fiscal year 2019, we continued to make effort to restart operations of the HTTR that stopped since the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. It is necessary for the HTTR reoperation to prove conformity with the new regulatory requirements for research reactors enacted in December 2013. So we might cope with government agency to pass the inspection of application document for the HTTR licensing. This report summarizes the activities carried out in the fiscal year 2019, which were the situation of the new regulatory requirements screening of the HTTR, the operation and maintenance of the HTTR, R&Ds relevant to commercial-scale HTGRs, the international cooperation on HTGRs and so on.